VASCULAR BUNDLE:
The bundle which consists of tissue like xylem and phloem is known as vascular bundle.
TYPES OF VASCULAR BUNDLES:
1)RADIALS:
The vascular bundle in which xylem and phloem are found in different radius is known as radial vascular bundle.It is the characteristics feature of root.
Eg:monocot and dicot root
2)CONJOINT:
Conjoint vascular bundle is a type of vascular bundle in which xylem and phloem are found in same radius or bundle.
Eg dicot or monocot stem
a)COLLATERAL:
This is the condition in which xylem lies towards innerside and phloem towards outer.
i)CLOSED COLLATERAL:
In this condition,cambium is absent.
Eg:monocot stem
ii)OPEN COLLATERAL:
In this condition,cambium is present.
Eg:dicot stem
b)BICOLLATERAL:
This is the condition where the phloem and cambium lie on both sides of the xylem.
Eg stem of cucurbita family
3)CONCENTRIC:
It is a type of vascular bundle where the xylem and phloem are found in concentric rings.It is of following type:
a)AMPHICRIBAL/HADROCENTRIC:
This is the condition where the xylem lies in the centre and phloem surrounds it.
Eg:fern
b)AMPHIVASAL/LEPTOCENTRIC:
This is the condition where the phloem lies in the centre and xylem surround it.
Eg:Yucca,dracaena
Technique:amphicirbal----Bahira----phloem
Amphivasal-----vitra----phloem
PATTERN SHOWN BY XYLEM:
TECHNIQUE:Take protoxylem as reference and define.
1)EXARCH:
Pattern shown by xylem in which protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem towards centre is known as exarch.
Eg:Monocot and dicot root
2)ENDARCH:
Pattern shown by xylem in which protoxylem lies towards the centre and metaxylem towards the periphery is called endarch.
Eg:monocot and dicot stem
3)MESARCH:
The condition in which protoxylem lies middle of metaxylem is knowm as mesarch.
Eg: Rachis and rhizome of certain fern
TERMS:
1)INTRAFASICULAR CAMBIUM:Cambium of vascular bundle
2)INTERFASICULAR CAMBIUM:Cambium between the vascular cambium
PLANTS ANATOMY:
1)ANATOMY OF DICOT ROOT:
The T.S. of dicot root shows the following internal structure listed below:
a)EPIBLEMA:
Epiblema is the outermost single layer compactly arranged and bears numerous root hairs but without cuticle.It is parenchymatous in nature.
b)CORTEX:
Cortex lies just below the epiblema which consists of several layer of parenchymatous tissue with intercelluar spaces.These tissues help in storage of food materials.
c)ENDODERMIS:
Endodermis is the single layered parenchymatous tissues with barrel shape and compactly arranged cells.the lateral walls becomes thick and waxy which prevents the flow of water and minerals to form Casparian Stripes.Some cells having thin wall lie just against the protoplasm through which water and mineral are passed into stellar r egion is called as passage cells.
egion is called as passage cells.
d)PERICYCLE:
Pericycle is single layer lying just below the endodermis.It helps to develop lateral roots,secondary meristem and cork cambium.
e)CONJUCTIVE TISSUE:
These are thin walled tissue that separates xylem and phloem in vascular bundle.
f)VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
Vascular cambium consists of xylem and phloem which lie on different radii i.e is of radial type.The protoxylem lies towards the periphery whereas metaxylem lies towards the center;thus xylem is of exarch.Xylem is composed of tracheids and vessels whereas phloem consits of sieve tube,companion cells and phloem parenchyma.The main function of these vascular element is conduction of mineral and water(xylem);and food material(phloem).Vascular bundles ranges from 2-6.
g)PITH:
Pith is centrally located groups of parenchymatous tissue.In dicot roots,it may be absent but if present is found in reduced form due to secondary growth.
2)ANATOMY OF MONOCOT ROOT:
The T.S. of monocot root shows the following internal structure list ed below:
ed below:
a)EPIBLEMA:
Epiblema is the outermost single layer compactly arranged and bears numerous root hairs but without cuticle.It is parenchymatous in nature.
b)CORTEX:
Cortex lies just below the epiblema which consists of several layer of parenchymatous tissue with intercelluar spaces.These tissues help in storage of food materials.A few layer of cortex just below the epidermis dies off when they get older and cutinize to form exodermis.
c)ENDODERMIS:
Endodermis is the single layered parenchymatous tissues with barrel shape and compactly arranged cells.the lateral walls becomes thick and waxy which prevents the flow of water and minerals to form Casparian Stripes.Some cells having thin wall lie just against the protoplasm through which water and mineral are passed into stellar region is called as passage cells.
d)PERICYCLE:
Pericycle is single layered structure in the form of ring lying just below the endodermis.It is parenchymatous in nature and helps to develop lateral roots.
e)CONJUCTIVE TISSUE:
These are thin walled tissue that separates xylem and phloem in vascular bundle.
f)VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
Vascular cambium consists of xylem and phloem which lie on different radii i.e is of radial type.The protoxylem lies towards the periphery whereas metaxylem lies towards the center;thus xylem is of exarch.Xylem is composed of tracheids and vessels whereas phloem consits of sieve tube,companion cells and phloem parenchyma.The main function of these vascular element is conduction of mineral and water(xylem);and food material(phloem).Vascular bundles ranges from 6-20.
g)PITH:
Pith is centrally located groups of parenchymatous tissue and is well developed.
3)ANATOMY OF DICOT STEM:
The T.S. of dicot stem shows the following internal structure:
a)EPIDERMIS:
Epidermis is the outermost layer which is made up of parenchymatous cells compactly arranged and consisting numerous hairs.It is covered by cuticle which helps to check excess transpiration and external injuries.
cells compactly arranged and consisting numerous hairs.It is covered by cuticle which helps to check excess transpiration and external injuries.
b)HYPODERMIS:
Below epidermis is few layers of collenchymatous cell called hypodermis.It helps in mechanical function.
c)CORTEX:
A immediate layer below hypodermis is made up of few layer of parenchymatous cells consisting intercellular space called cortex.It helps in storage of food.
d)ENDODERMIS:
Endodermis lie just below the cortex and is made up of single layer of parenchymatous cell which are barrel shaped and compactly arranged.It consists of starch grain and is also known as starch sheath.
e)PERICYCLE:
Pericycle lies just below the endodermis and consists of 2-3 layers of parencymatous or schlerchymatous tissue.
f)VASCULAR BUNDLES:
The vascular bundle which is in the form of ring consists of xylem and phloem.It is of conjoint,colateral and open type i.e xylem and phloem are separted by cambium.The protoxylem lies toward the centre whereas metaxylem towards the periphery.Thus the xylem is endarch.Xylem consists of tracheids,vessels,wood fibre and xylem parenchyma whereas phloem consists of sieve tube,companion cells ,phloem parenchyma and bast fibre.These vascular tissue helps in the conduction of water,minerals and synthesized food.
g)PITH:
Pith is centrally located group of parencymatous cells that helps to store food.It is well developed.
h)MEDULLARY RAYS:
Group of elongated parenchymatous cell that extend from pith to cortex region in between two vascular bundles is called medullary rays.It helps to exchange food material.
4)ANATOMY OF MONOCOT STEM:
The T.S of monocot stem shows the following internal tissue listed below:
a)EPIDERMIS:
Epidermis is the outermost layer which is made up of parenchymatous cells compactly arranged and is covered by cuticle which helps to check excess transpiration and external injuries.
b)HYPODERMIS:
Below epidermis is few layers of sclerenchymatous cell called hypodermis.It helps in mechanical function.
c)GROUND TISSUE:
Ground tissue is multilayered,parencymatous that extends from hypodermis to the centre of stem.It is not differentiated into cortex and stellar region(endodermis,pericycle and vascular bundle).
d)VASCULAR BUNDLES:
Vascular bundles are foind in scattered form.The smaller bundles are distributed towards the pheriphery while the larger distributed towards centre.Each vascular bundle consist of xylem and phloem covered by bundle sheath.The vascular bundle is conjoint,colateral and closed type(Remember mC3)i.e absence of cambium.The xylem is endarch.The xylem consists of large vessel known as metaxylem and smaller protoxylem called lysigenous cavity formed by the disintegration of some protoxylem elements.The phloem consists of sieve tube,companion cells and bast fibre.these vascular tissue helps in the conduction of water,mineral and food material.
e)PITH:
Pith is completely absent.
NOTE:Phloem parenchyma is absent in monocot stem.
SECONDARY GROWTH:
The increase in thickness or diameter of plant axis due to formation of secondary tissue by the activity of cork or vascular cambium in the extra stellar or stellar region is known as secondary growth.Secondary growth doesn't take place in Monocot stem due to absence of cambium except in Yucca,Dracaena which are exception.
PROCESS OF SECONDARY GROWTH: 1)FORMATION OF COMPLETE RING OF VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
some of the medullary rays cells mostly in the line of intrafasicular cambium becomes meristematic and forms a strip of interfasicular cambium.The intrafasicular cambium joins with interfasicular cambium forming a complete ring of vascular cambium known as cambium ring.
2)ACTIVITY OF VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
The vascular cambium consists of single row of ray initial and fusiform initials.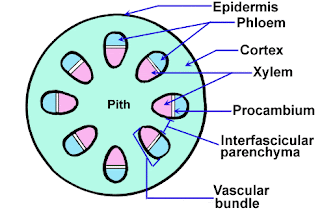
Ray initial forms parenchymatous medullary rays whereas fusiform initials form vascular elements xylem towards inner side and phloem toward outer side due to more activeness of vascular cambium in inner side than outer side.Fusiform initial divide periclinically giving rise to tissue mother cell which differentiate into secondary xylem cell inside the cambium and into secondary phloem outside the cambium.
In primary stem,primary xylem and primary phloem are nearer but due to formation of secondary xylem and phloem,they are shifted apart.Primary phloem are in the form of patches but later on they are crushed whereas primary xylem remain till the end in small amount at pith.
3)ANNUAL RING:
The activity of vascular cambium is not uniform due to climatic condition.The vascular cambium is more active during spring and is called spring wood whereas it is less active in autumn and is called autumn wood.Secondary xylem is more and larger in n umber in spring wood rather than in autumn wood.One spring wood and autumn wood forms annual ring.By counting the number of annual rings ,age of that particular part can be predicted and this process is known as dendrochronolgy.
umber in spring wood rather than in autumn wood.One spring wood and autumn wood forms annual ring.By counting the number of annual rings ,age of that particular part can be predicted and this process is known as dendrochronolgy.
4)SAP WOOD AND HEART WOOD:
The light colour wood formed on the outer side of tree in the late year which takes part in conduction is known as sap wood or alburminum.It is made of living as well as dead cell and is poor quality of wood.
The dark coloured wood formed on inner side of tree in the early year is known as heart wood or duranum.It is made of dead cell which is thickened.thus it does not take part in conduction.
take part in conduction.
5)ORIGIN AND ACTIVITY OF CORK CAMBIUM:
A strip of secondary meristem called cork cambium or phellogen commonly originates in the outer layer of the cortex.The activity of cork cambium gives up new cells on both sides forming the secondary cortex(phelloderm) towards the inner side and cork(phellem) on outer side.the secondary cortex generally contains chloroplast and carries photosynthesis while the cork found outside the cork cambium is roughly rectangular and consists of suberin which is impervious to water.That's why it is used in bottle cork.
BARK:
Bark is dead tissue lying outside the active cork cambium which include epidermis,lenticels and the cork.It function is to provide protection.
LENTICELS:
The aerating pores formed in bark through which exchange of gases take place are called lenticels.
SIGNIFICANCE OF SECONDARY GROWTH:
1)It provides support to increasing weight of aerial growth.
2)It produces corky bark and protects the interior part.
3)It adds new conducting tissue for replacement of old non functioning tissue.
The bundle which consists of tissue like xylem and phloem is known as vascular bundle.
TYPES OF VASCULAR BUNDLES:
1)RADIALS:
The vascular bundle in which xylem and phloem are found in different radius is known as radial vascular bundle.It is the characteristics feature of root.
Eg:monocot and dicot root
2)CONJOINT:
Conjoint vascular bundle is a type of vascular bundle in which xylem and phloem are found in same radius or bundle.
Eg dicot or monocot stem
a)COLLATERAL:
This is the condition in which xylem lies towards innerside and phloem towards outer.
i)CLOSED COLLATERAL:
In this condition,cambium is absent.
Eg:monocot stem
ii)OPEN COLLATERAL:
In this condition,cambium is present.
Eg:dicot stem
b)BICOLLATERAL:
This is the condition where the phloem and cambium lie on both sides of the xylem.
Eg stem of cucurbita family
3)CONCENTRIC:
It is a type of vascular bundle where the xylem and phloem are found in concentric rings.It is of following type:
a)AMPHICRIBAL/HADROCENTRIC:
This is the condition where the xylem lies in the centre and phloem surrounds it.
Eg:fern
b)AMPHIVASAL/LEPTOCENTRIC:
This is the condition where the phloem lies in the centre and xylem surround it.
Eg:Yucca,dracaena
Technique:amphicirbal----Bahira----phloem
Amphivasal-----vitra----phloem
PATTERN SHOWN BY XYLEM:
TECHNIQUE:Take protoxylem as reference and define.
1)EXARCH:
Pattern shown by xylem in which protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem towards centre is known as exarch.
Eg:Monocot and dicot root
2)ENDARCH:
Pattern shown by xylem in which protoxylem lies towards the centre and metaxylem towards the periphery is called endarch.
Eg:monocot and dicot stem
3)MESARCH:
The condition in which protoxylem lies middle of metaxylem is knowm as mesarch.
Eg: Rachis and rhizome of certain fern
TERMS:
1)INTRAFASICULAR CAMBIUM:Cambium of vascular bundle
2)INTERFASICULAR CAMBIUM:Cambium between the vascular cambium
PLANTS ANATOMY:
1)ANATOMY OF DICOT ROOT:

The T.S. of dicot root shows the following internal structure listed below:
a)EPIBLEMA:
Epiblema is the outermost single layer compactly arranged and bears numerous root hairs but without cuticle.It is parenchymatous in nature.
b)CORTEX:
Cortex lies just below the epiblema which consists of several layer of parenchymatous tissue with intercelluar spaces.These tissues help in storage of food materials.
c)ENDODERMIS:
Endodermis is the single layered parenchymatous tissues with barrel shape and compactly arranged cells.the lateral walls becomes thick and waxy which prevents the flow of water and minerals to form Casparian Stripes.Some cells having thin wall lie just against the protoplasm through which water and mineral are passed into stellar r
 egion is called as passage cells.
egion is called as passage cells.d)PERICYCLE:
Pericycle is single layer lying just below the endodermis.It helps to develop lateral roots,secondary meristem and cork cambium.
e)CONJUCTIVE TISSUE:
These are thin walled tissue that separates xylem and phloem in vascular bundle.
f)VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
Vascular cambium consists of xylem and phloem which lie on different radii i.e is of radial type.The protoxylem lies towards the periphery whereas metaxylem lies towards the center;thus xylem is of exarch.Xylem is composed of tracheids and vessels whereas phloem consits of sieve tube,companion cells and phloem parenchyma.The main function of these vascular element is conduction of mineral and water(xylem);and food material(phloem).Vascular bundles ranges from 2-6.
g)PITH:
Pith is centrally located groups of parenchymatous tissue.In dicot roots,it may be absent but if present is found in reduced form due to secondary growth.
2)ANATOMY OF MONOCOT ROOT:
The T.S. of monocot root shows the following internal structure list
 ed below:
ed below:a)EPIBLEMA:
Epiblema is the outermost single layer compactly arranged and bears numerous root hairs but without cuticle.It is parenchymatous in nature.
b)CORTEX:
Cortex lies just below the epiblema which consists of several layer of parenchymatous tissue with intercelluar spaces.These tissues help in storage of food materials.A few layer of cortex just below the epidermis dies off when they get older and cutinize to form exodermis.
c)ENDODERMIS:
Endodermis is the single layered parenchymatous tissues with barrel shape and compactly arranged cells.the lateral walls becomes thick and waxy which prevents the flow of water and minerals to form Casparian Stripes.Some cells having thin wall lie just against the protoplasm through which water and mineral are passed into stellar region is called as passage cells.
d)PERICYCLE:
Pericycle is single layered structure in the form of ring lying just below the endodermis.It is parenchymatous in nature and helps to develop lateral roots.
e)CONJUCTIVE TISSUE:

These are thin walled tissue that separates xylem and phloem in vascular bundle.
f)VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
Vascular cambium consists of xylem and phloem which lie on different radii i.e is of radial type.The protoxylem lies towards the periphery whereas metaxylem lies towards the center;thus xylem is of exarch.Xylem is composed of tracheids and vessels whereas phloem consits of sieve tube,companion cells and phloem parenchyma.The main function of these vascular element is conduction of mineral and water(xylem);and food material(phloem).Vascular bundles ranges from 6-20.
g)PITH:
Pith is centrally located groups of parenchymatous tissue and is well developed.
3)ANATOMY OF DICOT STEM:
The T.S. of dicot stem shows the following internal structure:
a)EPIDERMIS:
Epidermis is the outermost layer which is made up of parenchymatous
 cells compactly arranged and consisting numerous hairs.It is covered by cuticle which helps to check excess transpiration and external injuries.
cells compactly arranged and consisting numerous hairs.It is covered by cuticle which helps to check excess transpiration and external injuries.b)HYPODERMIS:
Below epidermis is few layers of collenchymatous cell called hypodermis.It helps in mechanical function.
c)CORTEX:
A immediate layer below hypodermis is made up of few layer of parenchymatous cells consisting intercellular space called cortex.It helps in storage of food.
d)ENDODERMIS:
Endodermis lie just below the cortex and is made up of single layer of parenchymatous cell which are barrel shaped and compactly arranged.It consists of starch grain and is also known as starch sheath.
e)PERICYCLE:
Pericycle lies just below the endodermis and consists of 2-3 layers of parencymatous or schlerchymatous tissue.
f)VASCULAR BUNDLES:

The vascular bundle which is in the form of ring consists of xylem and phloem.It is of conjoint,colateral and open type i.e xylem and phloem are separted by cambium.The protoxylem lies toward the centre whereas metaxylem towards the periphery.Thus the xylem is endarch.Xylem consists of tracheids,vessels,wood fibre and xylem parenchyma whereas phloem consists of sieve tube,companion cells ,phloem parenchyma and bast fibre.These vascular tissue helps in the conduction of water,minerals and synthesized food.
g)PITH:
Pith is centrally located group of parencymatous cells that helps to store food.It is well developed.
h)MEDULLARY RAYS:
Group of elongated parenchymatous cell that extend from pith to cortex region in between two vascular bundles is called medullary rays.It helps to exchange food material.
4)ANATOMY OF MONOCOT STEM:
The T.S of monocot stem shows the following internal tissue listed below:
a)EPIDERMIS:
Epidermis is the outermost layer which is made up of parenchymatous cells compactly arranged and is covered by cuticle which helps to check excess transpiration and external injuries.
b)HYPODERMIS:
Below epidermis is few layers of sclerenchymatous cell called hypodermis.It helps in mechanical function.
c)GROUND TISSUE:
Ground tissue is multilayered,parencymatous that extends from hypodermis to the centre of stem.It is not differentiated into cortex and stellar region(endodermis,pericycle and vascular bundle).

d)VASCULAR BUNDLES:
Vascular bundles are foind in scattered form.The smaller bundles are distributed towards the pheriphery while the larger distributed towards centre.Each vascular bundle consist of xylem and phloem covered by bundle sheath.The vascular bundle is conjoint,colateral and closed type(Remember mC3)i.e absence of cambium.The xylem is endarch.The xylem consists of large vessel known as metaxylem and smaller protoxylem called lysigenous cavity formed by the disintegration of some protoxylem elements.The phloem consists of sieve tube,companion cells and bast fibre.these vascular tissue helps in the conduction of water,mineral and food material.
e)PITH:
Pith is completely absent.
NOTE:Phloem parenchyma is absent in monocot stem.
SECONDARY GROWTH:
The increase in thickness or diameter of plant axis due to formation of secondary tissue by the activity of cork or vascular cambium in the extra stellar or stellar region is known as secondary growth.Secondary growth doesn't take place in Monocot stem due to absence of cambium except in Yucca,Dracaena which are exception.
PROCESS OF SECONDARY GROWTH: 1)FORMATION OF COMPLETE RING OF VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
some of the medullary rays cells mostly in the line of intrafasicular cambium becomes meristematic and forms a strip of interfasicular cambium.The intrafasicular cambium joins with interfasicular cambium forming a complete ring of vascular cambium known as cambium ring.
2)ACTIVITY OF VASCULAR CAMBIUM:
The vascular cambium consists of single row of ray initial and fusiform initials.

Ray initial forms parenchymatous medullary rays whereas fusiform initials form vascular elements xylem towards inner side and phloem toward outer side due to more activeness of vascular cambium in inner side than outer side.Fusiform initial divide periclinically giving rise to tissue mother cell which differentiate into secondary xylem cell inside the cambium and into secondary phloem outside the cambium.
In primary stem,primary xylem and primary phloem are nearer but due to formation of secondary xylem and phloem,they are shifted apart.Primary phloem are in the form of patches but later on they are crushed whereas primary xylem remain till the end in small amount at pith.
3)ANNUAL RING:
The activity of vascular cambium is not uniform due to climatic condition.The vascular cambium is more active during spring and is called spring wood whereas it is less active in autumn and is called autumn wood.Secondary xylem is more and larger in n
 umber in spring wood rather than in autumn wood.One spring wood and autumn wood forms annual ring.By counting the number of annual rings ,age of that particular part can be predicted and this process is known as dendrochronolgy.
umber in spring wood rather than in autumn wood.One spring wood and autumn wood forms annual ring.By counting the number of annual rings ,age of that particular part can be predicted and this process is known as dendrochronolgy.4)SAP WOOD AND HEART WOOD:
The light colour wood formed on the outer side of tree in the late year which takes part in conduction is known as sap wood or alburminum.It is made of living as well as dead cell and is poor quality of wood.
The dark coloured wood formed on inner side of tree in the early year is known as heart wood or duranum.It is made of dead cell which is thickened.thus it does not
 take part in conduction.
take part in conduction.5)ORIGIN AND ACTIVITY OF CORK CAMBIUM:
A strip of secondary meristem called cork cambium or phellogen commonly originates in the outer layer of the cortex.The activity of cork cambium gives up new cells on both sides forming the secondary cortex(phelloderm) towards the inner side and cork(phellem) on outer side.the secondary cortex generally contains chloroplast and carries photosynthesis while the cork found outside the cork cambium is roughly rectangular and consists of suberin which is impervious to water.That's why it is used in bottle cork.
BARK:
Bark is dead tissue lying outside the active cork cambium which include epidermis,lenticels and the cork.It function is to provide protection.
LENTICELS:
The aerating pores formed in bark through which exchange of gases take place are called lenticels.
SIGNIFICANCE OF SECONDARY GROWTH:
1)It provides support to increasing weight of aerial growth.
2)It produces corky bark and protects the interior part.
3)It adds new conducting tissue for replacement of old non functioning tissue.
No comments:
Post a Comment