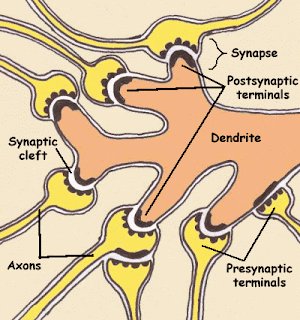
SYNAPSE AND NEUROTRANSMITTER:
There is always involvement of more than one neuron for the transmission of nerve impulse.It might be the sensory or motor.At the free end of axon,the axon branches as well as the terminal end swells.These swellings are known as Synaptic knobs or buttons.There is no physical contact between the two nerve cell that involve in action potential.The gap that is formed between pre synaptic neuron and post synaptic neuron is called Synaptic cleft and the process is called Synapse.
The synapse is an area of functional contact between one neuron and another for purpose of transferring information.Synapses are usually found between the line terminal branches of axon of a neuron and the dendrites or cell body of another.This type of neuron is called Axon dendrite synapse.Sir Charles Sherrington was the first person who used the term 'synapse the junction point between two neurons.
In synaptic knob,Vesicles that contain neurotransmitter are present.Specific neurotransmitter are released by exocytosis from presynaptic neuron which diffuses with dendrites or cell body of post synaptic neuron.These chemicals help in the transmission of nerve impulse.The dopamine,histamine,serotonin,adrenalin,nor adrenalin,gamma amino butalic acid(GABA) are the neurotransmitter of nervous system.
NERVE IMPULSE CONDUCTION:
Nerve impulse is defined as the sum total of physical and chemical disturbances created by stimulus in the nerve cell.It is also defined as electrochemical event that changes membrane potential of nerve fibre and causes transmission of stimulus from receptor to CNS and vice versa.
An impulse is initiated by stimulation of sensory nerve ending or by the passage of an impulse from another nerve.Transmission of impulse or action potential is due to movement of ions across the nerve cell membrane.During rest,the nerve cell membrane or axolemma is polarised due to the difference of concentration of ion across the membrane.This means that their is different electric charges on either side of membrane.This is called resting membrane potential.The charged electric potential of axolemma is called action potential.The main ions involved in nerve impulse conduction is Na+(main extracellular cation)and k+(the main intracellular ion)
In resting state the sodium are actively transported from axoplasm to extracellular fluid as a result the concentration of sodium inside or in axoplasm is almost negligible.During this period the concentration of sodium is 100 times more than that of axoplasm.This is due to the active movement of sodium and is termed as Na pump.When the stimulated Na pump stops and the permeability of axolemma inceases by which Na+ diffuses from extracellular fluid to axoplasm.This cause depolarisation.Dipolarisation is very rapid enabling the conduction of nerve impulse along the entire lenght of neuron in a few millisecond.
In myelinated neuron,the insulating properties of myelin sheath prevent the movement of ion.THerefore electrical charges across the membrane can only occur at node of Ranvior.When an impulse occur at one node ,dipolarisation passes along next node so that the flow of current appear to leap from one node to another.This is called Saltatory conduction.Myelinated fibre conduct impulse faster than unmyelinated fibre because saltatory conduction is faster than complete conduction.The fastest fibres can conduct impulses at the rate of 130m/s as in skeletal muscle while the slowest impulses travel at 0.5m/s,
No comments:
Post a Comment